What is Creatine?
Creatine Information to Help You Build Muscle Fast
Q:What is creatine?
Build Muscle and Burn Fat provides you with up to date creatine information to help you answer this question. By understanding what creatine is, you can make informed decision on purchasing quality creatine supplements to help you build muscle and burn fat.
What is Creatine and Where Does It Come From?
Creatine consists of three amino acids: arginine, glycine and methionine. Our bodies naturally produce creatine to supply our muscles with energy. After production in the kidneys, liver, and pancreas, creatine flows to our muscles via the blood stream.
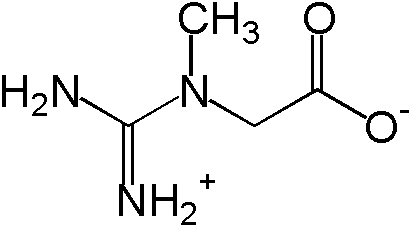
Once there, creatine acts like a gas pump for your muscles. In order to build muscle, your body converts creatine to creatine phosphate (phosphocreatine). So, then, what is creatine phosphate? It regenerates the muscle’s primary energy source, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This ATP is the fuel that powers your muscles. When working out, ATP is depleted rapidly. Creatine helps make new ATP to keep your muscles from running low.
What is Creatine? Creatine Information: The Science
On average, a 160 pound person stores approximately 120 grams of creatine in their bodies as creatine phosphate. 95 to 98% of this creatine is stored in your muscles.
Red meat (beef), herring, and salmon are all excellent sources of creatine; however, in order to obtain the amount of creatine found in powdered creatine supplements, you would need to literally eat pounds of these foods. That is where creatine supplements come in.
Higher Power Creatine 1000 grams - Only $19.99 at Bodybuilding.com!
Creatine comes in many varieties:
Creatine Information: How Does Creatine Help Build Muscle?
Q: How does creatine help in increasing muscle size?
A: Obviously, conversion to ATP is creatine’s primiary role in muscle building. However, there is some creatine information that indicates it may help build muscle in other ways.
Creatine pulls fluid into the muscle in a process commonly referred to "volumization." This increases the size of the muscle cells, and therefore the size of the muscle.
Additionally, there is some information that indicates that creatine buffer’s the amount of lactic acid that builds up in the muscle during exercise. Lactic acid causes that burning sensation in your muscle during exercise, and is foundation of the saying "No Pain, No Gain." The "pain" is from the lactic acid build up. So this important piece of creatine information indicates that we may be able to squeeze in a few more reps before that burning sensation kicks in. This means "More Gains Before the Pain!"
Creatine Information: Workouts are Essential to Build Muscle Fast
When we answered questions about creatine above, we mentioned that it consisted of three amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks used to build and repair muscle. As a result, creatine will not be effective for building muscle if you do not undertake a vigorous workout routine.
Creatine Information: Creatine Supplements
Often times, when someone asks the question "What is creatine ?" they are specifically referring to creatine supplements.
Even though the effects of creatine have been known for some time, creatine supplements did not become popular until around 1992. The two most popular types of creatine supplements are creatine monohydrate and creatine ethyl ester (CEE).
What is Creatine Monohydrate?
Creatine monohydrate is creatine bound with water. Each creatine molecule consists of 88% creatine with the remainder being water. It is the most common form of creatine supplement, and has the most widely available creatine information. Most studies on creatine have been done on this form of creatine supplement.
What is Creatine Ethyl Ester (CEE)?
Creatine Ethyl Ester (CEE) is a form of creatine which claims to have a better rate of absorption than creatine monohydrate. Basically, creatine ethyl ester is creatine monohydrate with an ester attached. Because it is more lipophilic, meaning that it dissolves more easily in fats and oils. The body converts creatine ethyl ester (CEE) back to creatine.
Leave "Creatine Information: What is Creatine?" and Return Home




